Understanding Asbestos: A Comprehensive Guide to a Controversial Material
Related Articles: Understanding Asbestos: A Comprehensive Guide to a Controversial Material
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding Asbestos: A Comprehensive Guide to a Controversial Material. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Asbestos: A Comprehensive Guide to a Controversial Material

Asbestos, a naturally occurring fibrous mineral, has a complex and controversial history. Once widely celebrated for its remarkable properties, it has become synonymous with danger and health risks. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of asbestos, exploring its characteristics, historical uses, health implications, and current management strategies.
What is Asbestos?
Asbestos is a group of six naturally occurring silicate minerals, each with distinct physical and chemical properties. These minerals are characterized by their fibrous structure, which gives them unique qualities like high tensile strength, heat resistance, and chemical stability.
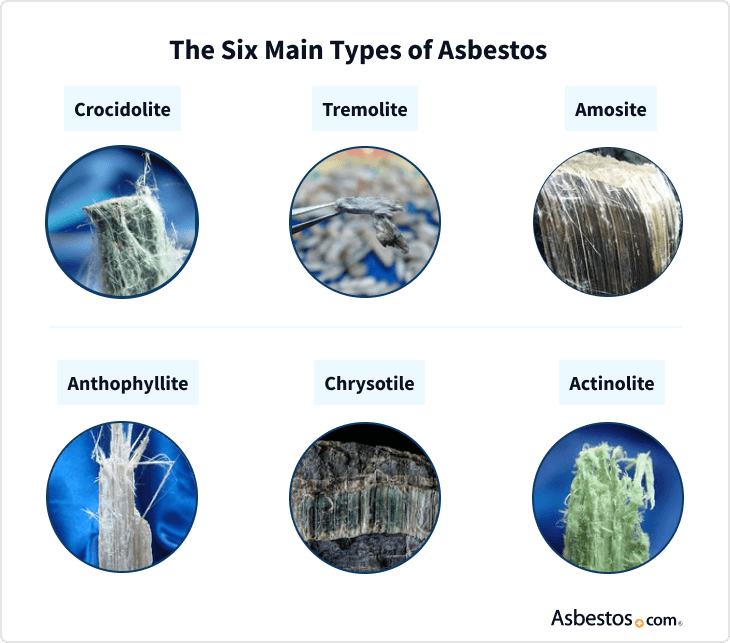
Types of Asbestos:
The six main types of asbestos are:
- Chrysotile: The most common type, known for its flexibility and resistance to heat.
- Amosite: Also known as "brown asbestos," it is more rigid and resistant to acids.
- Crocidolite: Known as "blue asbestos," it is the most dangerous type due to its thin and easily airborne fibers.
- Tremolite: A white asbestos with a needle-like structure.
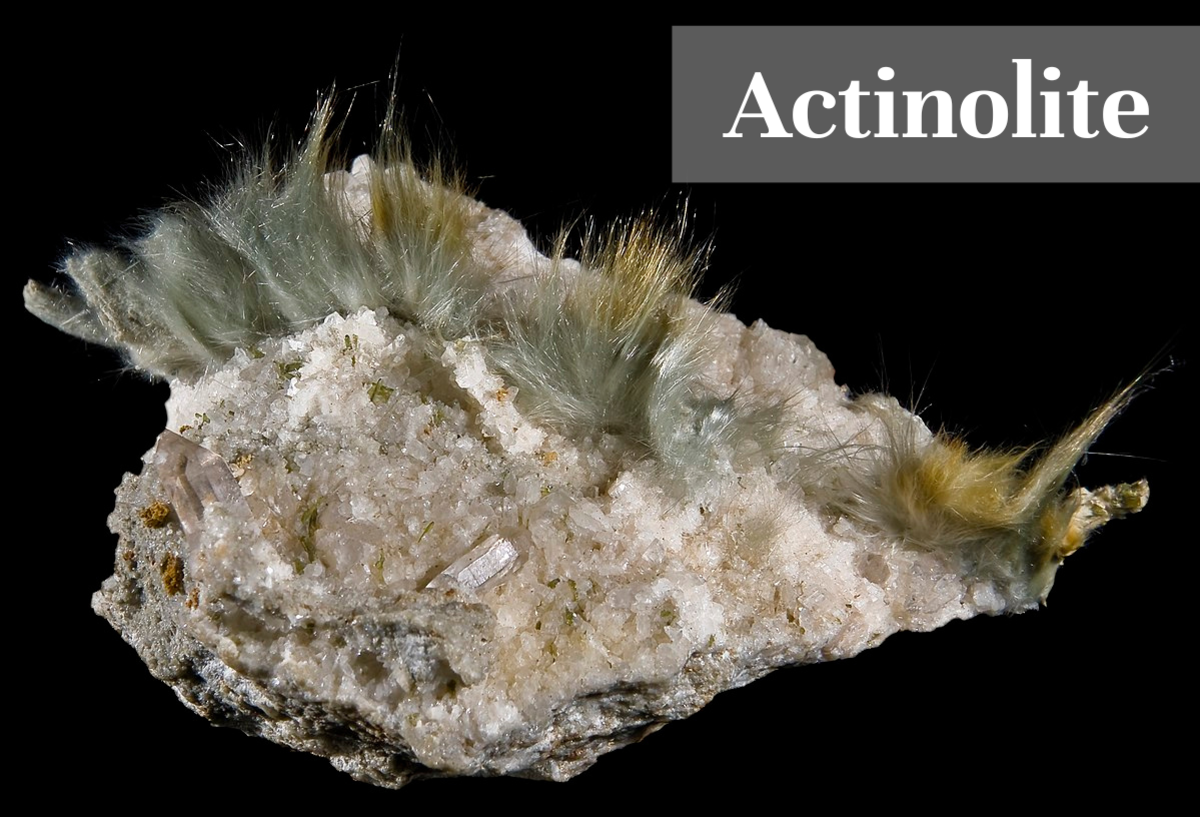
- Actinolite: Another white asbestos, often found mixed with other types.
- Anthophyllite: A brown asbestos with a fibrous structure.
Historical Uses of Asbestos:
Asbestos has been utilized for centuries due to its remarkable properties. Its resistance to heat, fire, and chemicals made it ideal for various applications:
- Construction: Asbestos was widely used in building materials like insulation, roofing shingles, floor tiles, and cement products.
- Automotive: It was incorporated into brake pads, clutch linings, and gaskets due to its heat resistance.
- Textiles: Asbestos fibers were woven into fire-resistant clothing, fabrics, and filters.
- Shipbuilding: It was used in insulation, fireproofing, and sealing materials.
- Electrical: Asbestos was incorporated into electrical wiring, insulation, and circuit boards.
Health Risks Associated with Asbestos:
While asbestos offers valuable properties, it poses significant health risks when its fibers are inhaled or ingested. These fibers are microscopic and can remain lodged in the lungs for extended periods, leading to various diseases:
- Asbestosis: A chronic lung disease characterized by scarring and inflammation, causing shortness of breath and difficulty breathing.
- Lung Cancer: Exposure to asbestos significantly increases the risk of developing lung cancer, particularly when combined with smoking.
- Mesothelioma: A rare and aggressive cancer of the lining of the lungs, chest, or abdomen, directly linked to asbestos exposure.
- Other Cancers: Asbestos exposure has also been linked to cancers of the larynx, ovary, stomach, and colon.
The Latency Period:
A crucial aspect of asbestos-related diseases is the latency period, the time between exposure and the onset of symptoms. This period can range from several years to decades, making it challenging to establish a direct link between exposure and illness.
Factors Influencing Health Risks:
Several factors influence the severity of asbestos-related health risks:
- Type of Asbestos: Crocidolite is considered the most dangerous due to its thin and easily airborne fibers.
- Duration of Exposure: Prolonged exposure increases the risk of developing asbestos-related diseases.
- Concentration of Fibers: Higher concentrations of asbestos fibers in the air lead to greater health risks.
- Individual Susceptibility: Some individuals may be more susceptible to asbestos-related diseases due to genetic factors or pre-existing conditions.
Managing Asbestos Risks:
Recognizing the health hazards posed by asbestos, numerous measures have been implemented to manage its risks:
- Regulation and Bans: Many countries have implemented regulations and bans on the use and production of asbestos, restricting its availability and minimizing exposure.
- Asbestos Removal: Trained professionals are employed to safely remove asbestos-containing materials from buildings and structures, minimizing the risk of fiber release.
- Encapsulation: In some cases, asbestos-containing materials are encapsulated with a sealant to prevent fiber release.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Workers handling asbestos must wear specialized PPE, including respirators, gloves, and protective clothing.
- Awareness and Education: Raising awareness about the dangers of asbestos and educating individuals about safe handling practices are crucial for minimizing exposure.
FAQs about Asbestos:
Q: Is asbestos still used today?
A: While the use of asbestos has been significantly reduced in many countries, it is still used in some developing nations due to its low cost and availability.
Q: How can I tell if a building contains asbestos?
A: It is difficult to visually identify asbestos-containing materials. Professional testing is required to determine the presence and type of asbestos in a building.
Q: Is asbestos dangerous if it is not disturbed?
A: Asbestos poses a risk only when its fibers are released into the air. However, even undisturbed asbestos can become a hazard during renovations, demolition, or natural disasters.
Q: What should I do if I suspect asbestos in my home?
A: Contact a qualified asbestos inspector or removal contractor to assess the situation and recommend appropriate action.
Q: Can asbestos be cleaned up safely?
A: Asbestos removal requires specialized training and safety protocols. Attempting to clean up asbestos yourself is highly discouraged and can be extremely dangerous.
Tips for Dealing with Asbestos:
- Avoid disturbing asbestos-containing materials.
- Hire professionals for asbestos removal or encapsulation.
- Follow all safety precautions during asbestos handling.
- Keep children and pets away from areas where asbestos is present.
- Regularly inspect your home for signs of asbestos damage.
Conclusion:
Asbestos is a complex material with both beneficial and detrimental aspects. While its remarkable properties have been utilized for various applications, its potential for causing serious health problems cannot be ignored. Understanding the risks associated with asbestos, implementing proper management strategies, and prioritizing safety are crucial to protecting public health. By recognizing the historical significance of asbestos and acknowledging its current limitations, we can navigate its use responsibly and minimize its impact on human health.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Asbestos: A Comprehensive Guide to a Controversial Material. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!